Redshift Warehouse Destination
This guide explains the process to provision a Redshift cluster and allow the Segment warehouse connector to write to it.
Getting Started
Complete the following steps to provision your Redshift cluster, and connect Segment to it:
- Choose the best instance for your needs
- Provision a new Redshift Cluster
- Create a database user
- Connect Redshift to Segment
View observability metrics about your Redshift Warehouse Destination with Delivery Overview
Delivery Overview, Segment’s built-in observability tool, is now in public beta for storage destinations. For more information, see the Delivery Overview documentation.
Choose the best instance for your needs
While the number of events (database records) are important, the storage capacity usage of your cluster depends primarily on the number of unique tables and columns created in the cluster. Keep in mind that each unique .track() event creates a new table, and each property sent creates a new column in that table. To avoid storing unnecessary data, start with a detailed tracking plan before you install Segment libraries to ensure that only the necessary events are passed to Segment.
Redshift gives the option of three cluster types:
- Dense Compute: These clusters are designed to maximize query speed and performance at the expense of storage capacity. This is done by using fast CPUs, large amounts of RAM and solid-state storage. While there are no hard and fast rules for sizing a cluster, customers with fewer than 20 million monthly events should start with a single DC1 node cluster and add nodes as needed. A single node cluster includes 200GB, with a max size of 2.56TB.
- Dense Storage These clusters are designed to maximize the amount of storage capacity for customers who have 100s of millions of events and prefer to save money on Redshift hosting costs. This is done by using slower CPUs, less RAM, and disk-based storage. A single DS2 node cluster includes 2TB of space, with a max size of 16TB.
- RA3: These clusters provide managed storage to help optimize your data warehouse splitting the cost of compute and storage.
Provision a new Redshift Cluster
Follow the steps below to create a new Redshift cluster. If you have a cluster already provisioned, skip this step.
-
From the Redshift dashboard, click Create Cluster.
-
Name your new cluster, and select the type and size of the nodes within the cluster.

-
Configure the database connection details and admin user for the cluster.

Now that you’ve provisioned your Redshift cluster, you’ll need to configure your Redshift cluster to allow Segment to access it.
Create a Database User
The username and password you’ve already created for your cluster is your admin password, which you should keep for your own use. For Segment, and any other 3rd-parties, it is best to create distinct users. This allows you to isolate queries from one another using WLM and perform audits easier.
To create a new user, log into the Redshift cluster directly (using the credentials you defined in Step 3 above) and run the following SQL commands:
-- create a user named "segment" that Segment will use when connecting to your Redshift cluster.
CREATE USER segment PASSWORD '<enter password here>';
-- allows the "segment" user to create new schemas on the specified database. (this is the name you chose when provisioning your cluster)
GRANT CREATE ON DATABASE "<enter database name here>" TO "segment";
When you configure your warehouse in Segment, use the username/password you’ve created here instead of your admin account.
Connect Redshift to Segment
Unified warehouse credentials in public beta
With unified warehouse credientials you can create warehouse credentials and use them across Segment warehouse products. Segment is actively working on this feature. Some functionality may change before it becomes generally available.
To connect Redshift to Segment:
- Navigate to your product area in the Segment app:
- For Storage destinations, navigate to Connections > Destinations and select the Storage tab. Click + Add storage destination.
- For Profiles Sync, navigate to Unify > Profiles Sync.
- Select Redshift as your warehouse.
- Select an existing warehouse credential or create a new warehouse credential by completing the following fields for your Redshift instance:
- Hostname: The Redshift URL
- Port: The port used for connecting to your Redshift warehouse
- Database name: The database that Segment uses in order to sync data
- Username: The Redshift user that Segment uses to run SQL in your warehouse
- Password: The password of the user above
- Test your connection.
- Click Save.
Security
VPC
VPCs keep servers inaccessible to traffic from the internet. With VPC, you’re able to designate specific web servers access to your servers. In this case, you will be whitelisting the Segment IPs to write to your data warehouse.
SSL/TLS
Always require SSL/TLS and make sure your data warehouse accepts only secure connections. Segment only connects to your data warehouse using SSL/TLS.
Allowlisting IPs
Segment recommends enabling IP allowlists for added security. All Segment users with workspaces hosted in the US who use allowlists in their warehouses must update those allowlists to include the following ranges:
52.25.130.38/3234.223.203.0/28
Users with workspaces in the EU must allowlist 3.251.148.96/29.
Best practices
Networking
Redshift clusters are created in a VPC subnet. To configure:
-
Navigate to the Redshift cluster you created previously. Click Edit.
-
Expand the Network and security section and click Open tab to access the Network and security settings.

-
Click the VPC security group to access its settings. The Security group opens in a new tab.

-
Click the Security group in the list to access its settings.
-
On the Inbound tab, add rules to enable Segment to write to your Redshift port from
34.223.203.0/28and52.25.130.38/32.
-
On the Outbound tab, ensure Redshift can make outbound requests to the Segment S3 bucket. The default behavior is to allow all outbound traffic, but security groups can limit outbound behavior.

-
Navigate back to the cluster’s settings, and click Edit publicly accessible to allow access to the cluster from outside of the VPC.

Electing to encrypt data
You can encrypt data in the Redshift console. Encryption does not affect Segment’s ability to read or write.
Distribution Key
The id column is the common distribution key used across all tables. When you execute a query, the Redshift query optimizer redistributes the rows to the compute nodes as needed to perform any joins and aggregations. The goal in selecting a table distribution style is to minimize the impact of the redistribution step by locating the data where it needs to be before the query is executed.
Reserved Words
Redshift limits the use of reserved words in schema, table, and column names. Additionally, avoid naming traits or properties that conflict with top level Segment fields (for example, userId, receivedAt, or messageId). These traits and properties that conflict with Redshift or Segment fields are _-prefixed when Segment creates columns for them in your schema.
Redshift limits the use of integers at the start of a schema or table name. Segment prepends an underscore _ to any schema, table or column name that starts with an integer. A source named 3doctors is loaded into a Redshift schema named _3doctors.
CPU
In a usual workload Redshift around 20-40% of CPU. Segment takes advantage of the COPY command to make full use of your cluster to load your data as efficiently as possible.
Troubleshooting
How do I improve Query Speed?
The speed of your queries depends on the capabilities of the hardware you have chosen as well as the size of the dataset. The amount of data use in the cluster will also impact query speed. For Redshift clusters, if you’re above 75% capacity, you will likely experience degradation in query speed. Here’s a guide on how to improve your query speeds.
FAQ
How do I sync data in and out between Redshift and Segment?
It’s often the case that customers want to combine 1st-party transactional and operational data with Segment data to generate a full view of the customer. The challenge is that those data sets are often stored in separate data warehouses.
If you’re interested in importing data into a Redshift cluster, it’s important that you follow these guidelines.
Additionally, there a number of tools which provide syncing services between databases (mySQL, SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL). Here is a list of some that Segment customers use.
You can also unload data to a s3 bucket and then load the data into another Redshift instance manually.
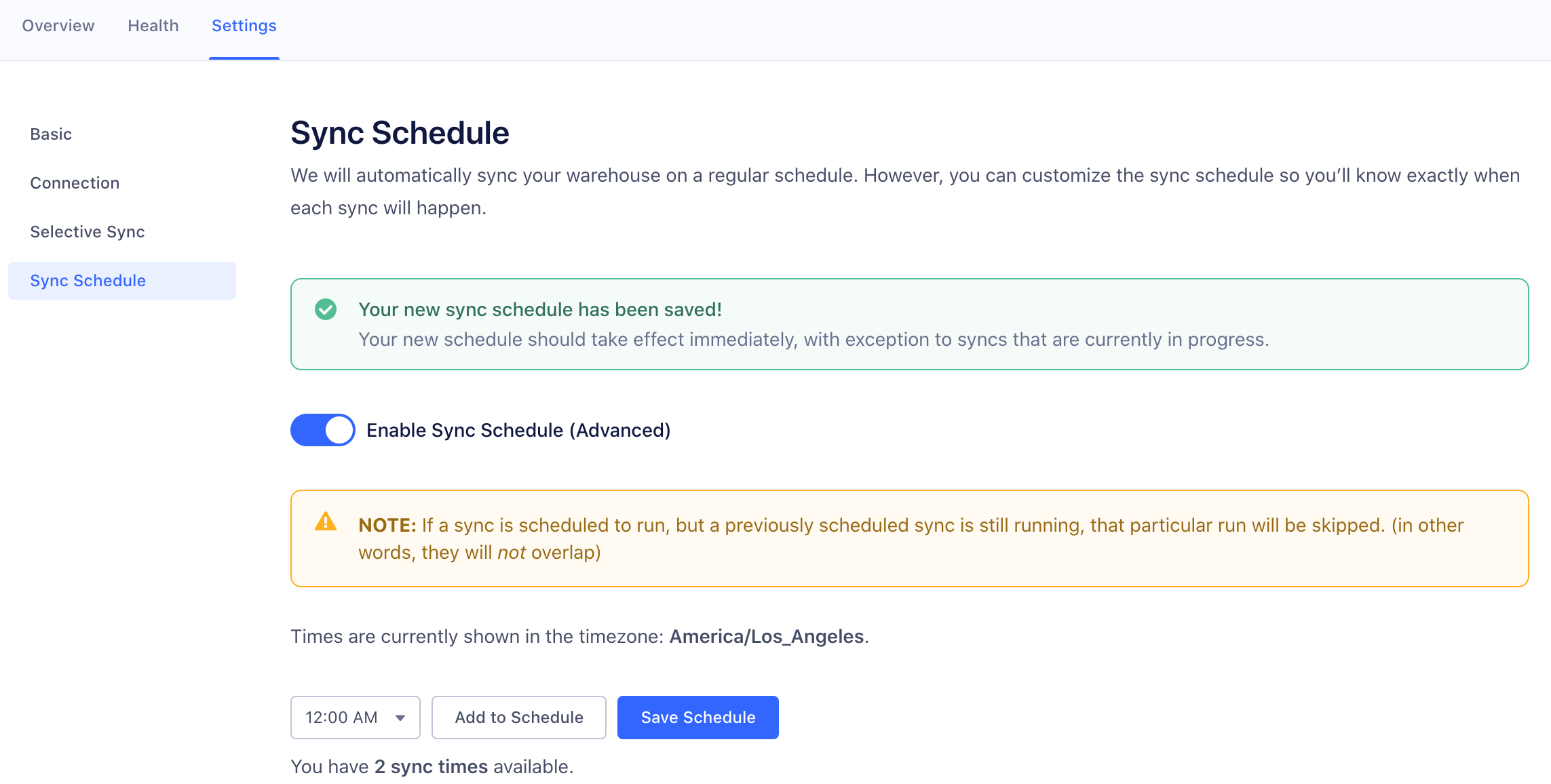
Can I customize my sync schedule?
Your data will be available in Warehouses between 24 and 48 hours from your first sync. Your warehouse then syncs once or twice a day depending on your Segment Plan.
Segment allows Business Tier (BT) customers to schedule the time and frequency of warehouse data syncs.
If you are on a BT plan, you can schedule warehouse syncs by going to Warehouse > Settings > Sync Schedule in the Segment web app. You can schedule up to the number of syncs allowed on your billing plan.
Can I use an SSH tunnel to connect to my Redshift instance?
Segment does not currently support SSH tunneling to Redshift. You can usually allow Segment’s ETL to write to Redshift without leaving the cluster available to other connections by using IP level restrictions.
Segment supports several layers of Redshift’s security model:
- Security groups: Security groups control the incoming and outgoing traffic to a resource. You can think of this like a pinhole in a firewall that only allows traffic from Segment’s IP address. Security groups are a fundamental building block of AWS security.
- SSL: This secures data in transit and allows Segment to validate that the warehouse at the other end is actually a warehouse owned by AWS. This is especially important if your Redshift warehouse is not located in the
us-west-2region. - Username and password: This is the basic method used to authenticate database users and apply varying levels of permissions - for example, who can create tables, who can delete data, who can see which tables.
Do you support Redshift Serverless?
Segment does not currently support Serverless Redshift. While you can set up the connection in the Segment app, Segment does not have the functionality to query Redshift’s SYS tables.
How can I change the host for an existing Redshift destination?
Segment recommends that you first disable the sync for the warehouse, check that the syncs that are in progress have stopped/finished, and then update the host. Once you’ve updated the host, you can then re-enable the sync.
The Segment connector picks up where the last completed sync left off, and does not sync any historical data with the new host. The historical data that occurred when you were updating the host needs to be backfilled to your new connection using the Replay Feature. Replays are currently only available for Business Tier customers. Contact Segment Support and Segment’s Success Engineers will be able to assist you with a Replay.
This page was last modified: 18 Sep 2025
Need support?
Questions? Problems? Need more info? Contact Segment Support for assistance!